The brain is one of the most complex and vital organs in the human body. It acts as the control center for all bodily functions, thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. The brain is responsible for processing information, making decisions, and controlling actions.
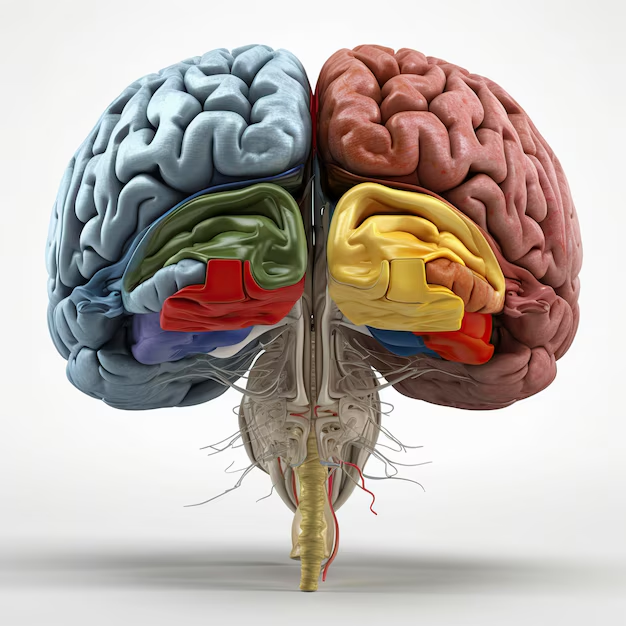
The brain is divided into several key parts, each with distinct functions:
- Cerebrum: The largest part of the brain, responsible for higher brain functions such as thought, memory, emotion, and voluntary movement. It’s divided into two hemispheres (left and right) and further into four lobes:
- Frontal Lobe: Involved in decision-making, problem-solving, planning, and voluntary movement.
- Parietal Lobe: Processes sensory information such as touch, temperature, and pain.
- Temporal Lobe: Involved in hearing, language processing, and memory.
- Occipital Lobe: Responsible for visual processing.
- Cerebellum: Located at the back of the brain, it coordinates voluntary movements, balance, and posture.
- Brainstem: Connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls vital functions such as heart rate, breathing, and digestion. It consists of three parts:
- Midbrain: Involved in vision, hearing, and eye movement.
- Pons: Connects the cerebrum and cerebellum and plays a role in sleep and arousal.
- Medulla Oblongata: Regulates vital functions like heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure.
- Limbic System: A group of structures involved in emotions, memory, and motivation. Key components include:
- Amygdala: Processes emotions such as fear and pleasure.
- Hippocampus: Essential for memory formation and spatial navigation.
- Thalamus: Acts as a relay station for sensory information.
- Hypothalamus: Regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst, and other autonomic functions.
Functions of the Brain
- Cognition: The brain is responsible for thinking, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
- Sensation and Perception: It processes sensory information from the body, such as sight, sound, touch, taste, and smell.
- Motor Control: The brain controls voluntary movements and coordination of muscles.
- Emotion and Behavior: It regulates emotions, moods, and social behaviors.
- Memory: The brain encodes, stores, and retrieves information, allowing us to learn and remember.
- Autonomic Functions: It regulates involuntary functions such as heart rate, breathing, and digestion.
Protecting Brain Health
- Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals to support brain health.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity improves blood flow to the brain, promotes neurogenesis (the growth of new neurons), and enhances cognitive function.
- Mental Stimulation: Engage in activities that challenge your brain, such as reading, puzzles, learning new skills, and social interactions.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get enough quality sleep to support memory consolidation, mood regulation, and overall brain function.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness to reduce stress and its impact on the brain.
Fun Fact
Did you know that the human brain consists of approximately 86 billion neurons?
These neurons communicate through trillions of connections called synapses, enabling the brain to process vast amounts of information simultaneously.
The brain’s complexity and adaptability make it one of the most fascinating organs in the human body. By taking care of your brain through a healthy lifestyle and mental stimulation, you can support its function and well-being throughout your life.
