Cardio (short for cardiovascular exercise) and endurance training are two critical components of a well-rounded fitness regimen, especially for improving heart health, stamina, and overall physical performance.
Cardio (Cardiovascular Exercise)
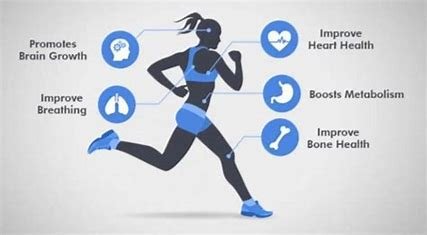
What is Cardio? Cardio refers to any exercise that raises your heart rate and engages your cardiovascular system—your heart, lungs, and blood vessels. These exercises improve the efficiency of your heart and lungs, increase oxygen delivery throughout the body, and help improve overall cardiovascular health.
Types of Cardio:
- Steady-State Cardio: This involves maintaining a consistent intensity over a prolonged period, such as jogging, cycling, swimming, or walking.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): A form of cardio where you alternate between short bursts of intense activity followed by brief periods of rest or low-intensity movement. Examples include sprints, jump rope, or burpees.
- Low-Intensity Steady-State (LISS): A lower-intensity form of steady-state cardio, like a brisk walk or light cycling, usually done for a longer duration.
- Circuit Training: A combination of resistance exercises and short bursts of cardio exercises, like jumping jacks or running in place, performed in a sequence.
Benefits of Cardio:
- Improved Heart Health: Regular cardio strengthens the heart, improves blood circulation, and helps lower blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Increased Calorie Burn: Cardio helps you burn calories, which aids in fat loss and weight management.
- Boosted Mood: Cardio releases endorphins, which are chemicals in the brain that improve mood and reduce stress.
- Increased Lung Capacity: By working your respiratory system, cardio improves lung function and increases stamina.
- Better Sleep: Regular cardiovascular exercise helps improve sleep quality.
Endurance Training
What is Endurance? Endurance refers to the ability to sustain prolonged physical or mental effort. In fitness, endurance training focuses on improving your body’s ability to perform a particular activity for extended periods without tiring. There are two main types of endurance:
- Aerobic Endurance: The ability to perform low to moderate intensity activity for a prolonged period. This is typically associated with cardiovascular activities like long-distance running, swimming, or cycling.
- Muscular Endurance: The ability of a muscle or group of muscles to perform repetitive contractions without fatigue. For example, performing high-repetition weightlifting (like doing 20-30 reps of squats or push-ups) to target the endurance of specific muscles.
Benefits of Endurance Training:
- Increased Stamina: Over time, your body adapts to longer and more intense physical activity, allowing you to exercise longer or at higher intensities before fatigue sets in.
- Enhanced Performance: Whether you’re training for a marathon, a race, or a sport, endurance training can improve your performance by allowing you to sustain energy for longer periods.
- Improved Oxygen Utilization: Endurance training increases the efficiency of oxygen delivery to muscles, which is essential for both cardio and strength performance.
- Reduced Fatigue: By improving your overall endurance, you become less fatigued by everyday activities and can recover more quickly between workouts.
- Mental Toughness: Endurance training teaches you to push through physical discomfort, improving your mental resilience and determination.
How Cardio and Endurance Work Together
Cardio and endurance training go hand in hand, as both help improve the body’s ability to perform over extended periods. Here’s how:
- Improved Aerobic Capacity: Cardio, particularly steady-state exercises like jogging or swimming, builds aerobic endurance by teaching your body to efficiently transport and use oxygen during exercise. The longer you can sustain activity, the more endurance you have.
- Higher Performance: As you build both aerobic endurance (through cardio) and muscular endurance (through strength or bodyweight exercises), you improve your ability to maintain a higher level of performance for a longer time. This is useful in endurance sports, as well as activities like hiking, running, or cycling.
- Faster Recovery: Cardio and endurance training help your body recover quicker between intense bouts of exercise. For example, the improved efficiency of your heart and lungs from regular cardio exercise helps you recover faster after a sprint, long run, or strength training session.
- Fat Burning: Combining cardio with endurance training can also help increase the body’s ability to burn fat for energy, especially when doing longer-duration, moderate-intensity activities.
Cardio and Endurance Training Tips
- Start Gradually: If you’re new to cardio or endurance training, start with moderate-intensity activities and gradually build up your intensity or duration. For example, start with brisk walking before progressing to running.
- Mix Up Your Workouts: Incorporate a mix of steady-state cardio (like jogging) and interval training (like sprints) to challenge your body in different ways and improve both aerobic and anaerobic endurance.
- Progressive Overload: Just like with strength training, you’ll need to progressively increase the intensity, duration, or frequency of your cardio and endurance workouts to continue making progress. For example, increase the duration of your runs each week or add intervals to your routine.
- Cross-Train: To prevent injury and keep workouts exciting, try different forms of cardio (running, cycling, swimming, etc.) and endurance exercises (e.g., bodyweight circuits, long hiking, etc.). This keeps the muscles challenged in different ways.
- Rest and Recovery: Allow your body to recover between intense sessions, especially if you’re doing high-intensity cardio or long endurance training. Rest days help prevent burnout and improve overall performance.
Sample Cardio and Endurance Workouts
For Cardio:
- HIIT Workout:
- 30 seconds of burpees
- 30 seconds of rest
- 30 seconds of jump squats
- 30 seconds of rest
- Repeat for 20-30 minutes.
- Steady-State Cardio:
- 30-45 minutes of moderate-intensity jogging or cycling at a steady pace.
- LISS (Low-Intensity Steady-State):
- 45-60 minutes of walking at a moderate pace.
For Endurance:
- Muscular Endurance Circuit (Bodyweight):
- 15 push-ups
- 20 bodyweight squats
- 25 walking lunges (each leg)
- 1-minute plank
- Rest for 1-2 minutes, repeat for 3-5 rounds.
- Endurance Running:
- Start with a 10-minute warm-up jog.
- Run at a steady pace for 30-45 minutes, trying to maintain consistent effort throughout.
